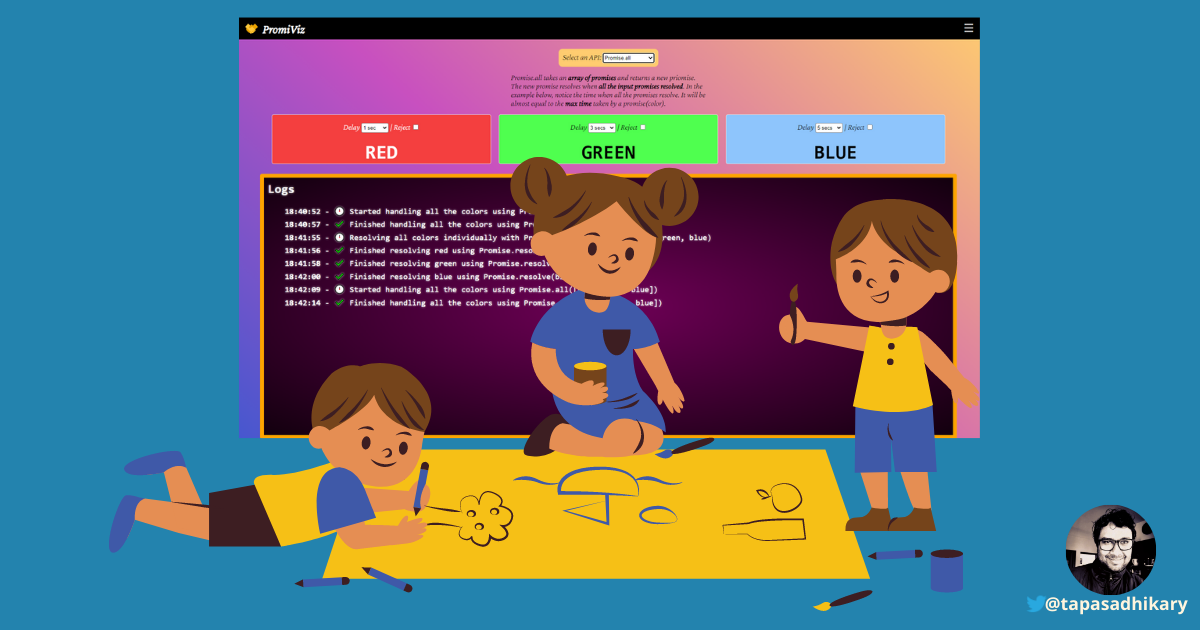
Introducing PromiViz - visualize and learn JavaScript promise APIs
A picture is worth of thousand words. Millions of pictures come together to make visuals. Let's visually learn about promise APIs. Please read on.
Why does JavaScript promise sounds a bit more complex than many other topics? Besides the factors that we have already discussed, we also need to know how it executes, what's the background story? After spending a considerable amount of time practicing and thinking about the promises using pen and paper, I got an idea to make a simple yet powerful tool for developers.
Meet PromiViz
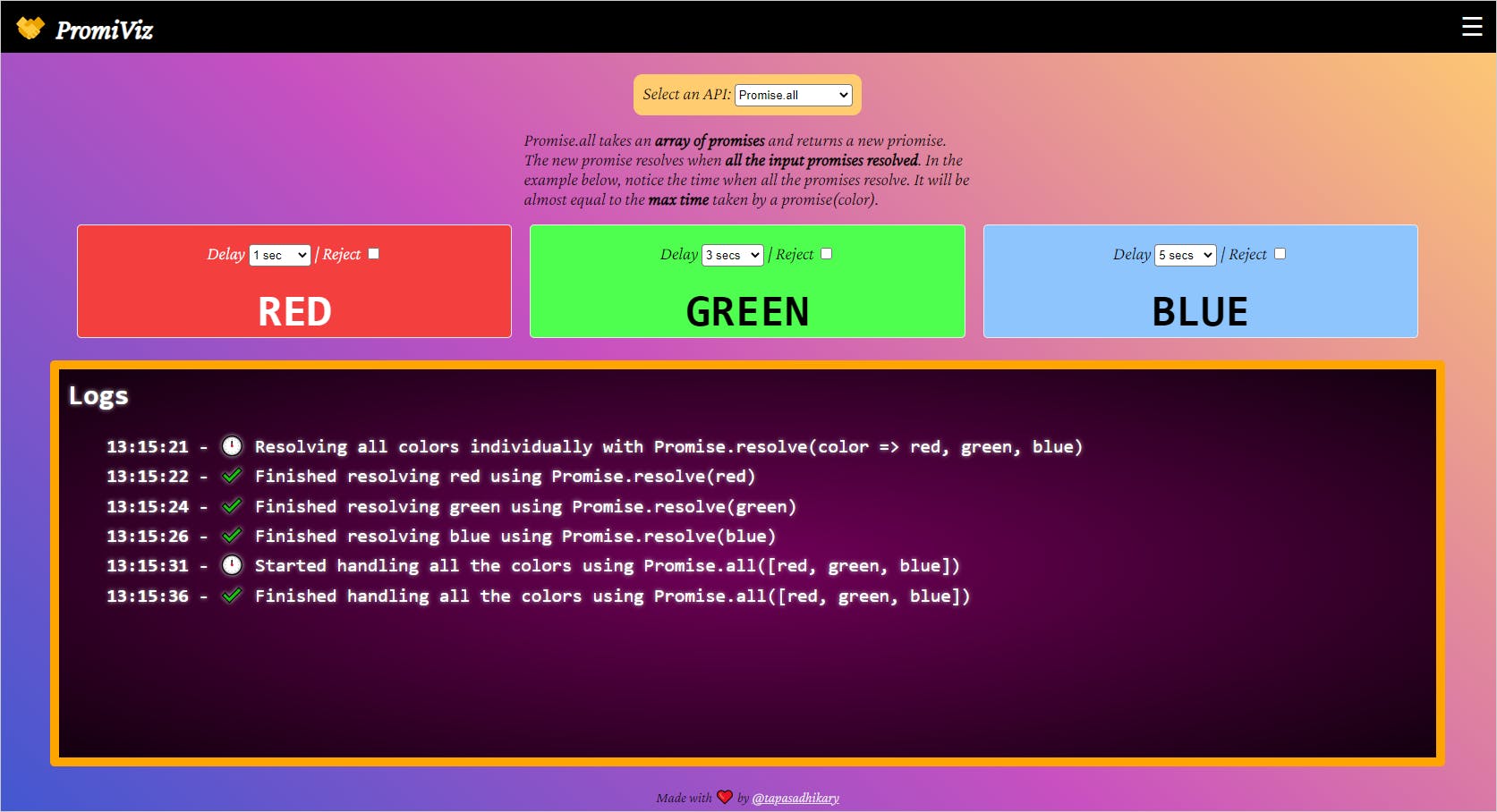
Promiviz is an open-source tool to try out the promise methods in intuitive ways. You can configure promises with delays, rejections and run them to see what's exactly happening behind the scene. It captures the log of each of the operations so that your understanding gets firmed as you use it. It is a tool for developers by a developer!
Please check out this short video to know more about the tool.
Here are the important links:
- The app: https://promiviz.vercel.app/
- GitHub Repo: https://github.com/atapas/promiviz
In this article, we will learn the Promise API methods using the PromiViz tool.
JavaScript Promise APIs
The Promise object in JavaScript has six practical methods that serve several use cases.
- Promise.all
- Promise.any
- Promise.race
- Promise.allSettled
- Promise.resolve
- Promise.reject
These methods take one or more promises as input and return a new promise to find the result or error. The first four methods are significant when it comes to handling multiple promises.
To demonstrate examples for each of these methods, we will use three promises. Each of these promises resolves with a color name, red, green, and blue respectively,
// It resolves with the value red after 1 second
const red = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('red');
}, 1000);
});
// It resolves with the value green after 3 seconds
const green = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('green');
}, 3000);
});
// It resolves with the value blue after 5 seconds
const blue = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('blue');
}, 5000);
});
Promise.all
The method Promise.all executes multiple promises in parallel and returns a new promise. It waits for the execution of all the premises to complete. So, the execution time of the Promise.all method will be the same as the max time taken by an input promise.
Let's use our example promises(red, green, and blue) to explain the Promise.all method.
const testAll = async () => {
const colors = await Promise.all([red, green, blue]);
console.log(colors);
colors.forEach(color => {
console.log(color);
});
}
testAll();
Here we use the async/await keywords. As the Promise.all method returns a new promise, we use the await keyword in front of it. By rule, we must use an async keyword for a function that uses await in it.
The variable colors is an array with all the resolved values,

A few points to consider here,
- The total time needs to execute the
Promise.allmethod is 5 seconds. Thebluepromise takes the max time(5 secs) to complete. - The resulting array has the resolved value in the same order of the promises passed to the
Promise.allmethod. - If any of the input promises reject(or error out), the
Promise.allrejects immediately. It means the rest of the input promises do not execute.
Let's try these with Promiviz. First, execute the Promise.all API and observe the output in the log window.
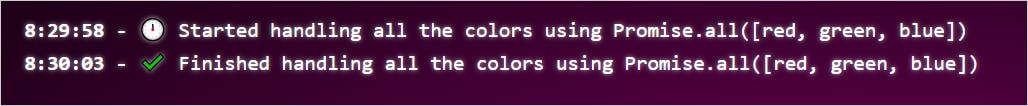
Have a look at the execution time there. It took 5 seconds. That is the time the blue promise took to finish. Now let's reject a promise, say, the green one!
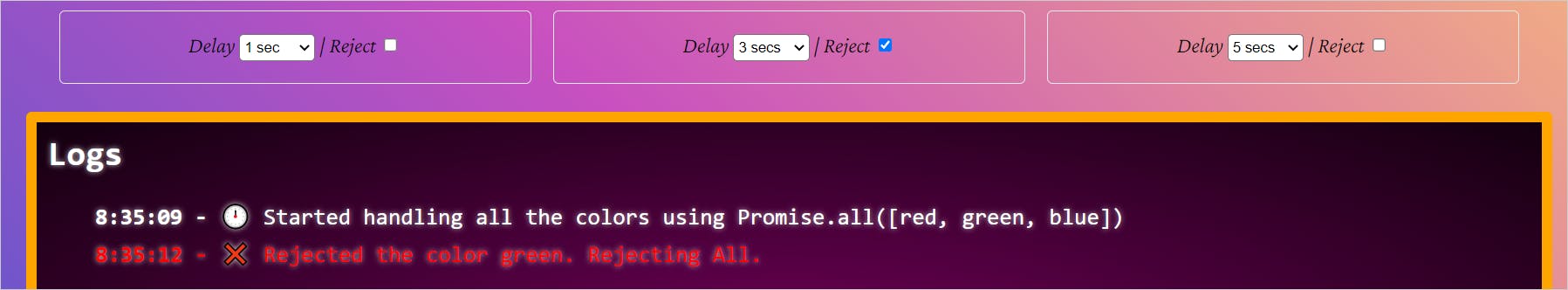
Again, look at the time in the log window. The Promise.all is rejected within 3 seconds(the time green takes to execute). It didn't even wait for the blue promise to execute.
Frequent mistake: All the input promises run parallel with the
Promise.allmethod. Hence the total time to execute all the promises successfully is NOT the sum of their time. It is the max time taken by an input promise. In our example, it is 5 seconds(time taken byblue), not 9 seconds(1 + 3 + 5).
Let's move onto the following promise API method.
Promise.any
Similar to Promise.all, the any method also takes a collection of input promises. However, it returns a new promise when any of the input promises is fulfilled.
const testAny = async () => {
const color = await Promise.any([red, green, blue]);
console.log(color);
}
testAny();
In this case, the first promise, red takes the least time to execute and resolves. Hence the output will be red.
A few points to consider,
- If any of the input promises are rejects or errors out, the
Promise.anymethod continues to execute other promises. - If all of the input promises reject, the
Promise.anymethod rejects withAggregateError.
Let's try these using PromiViz. Select the Promise.any API method and observe the log window.
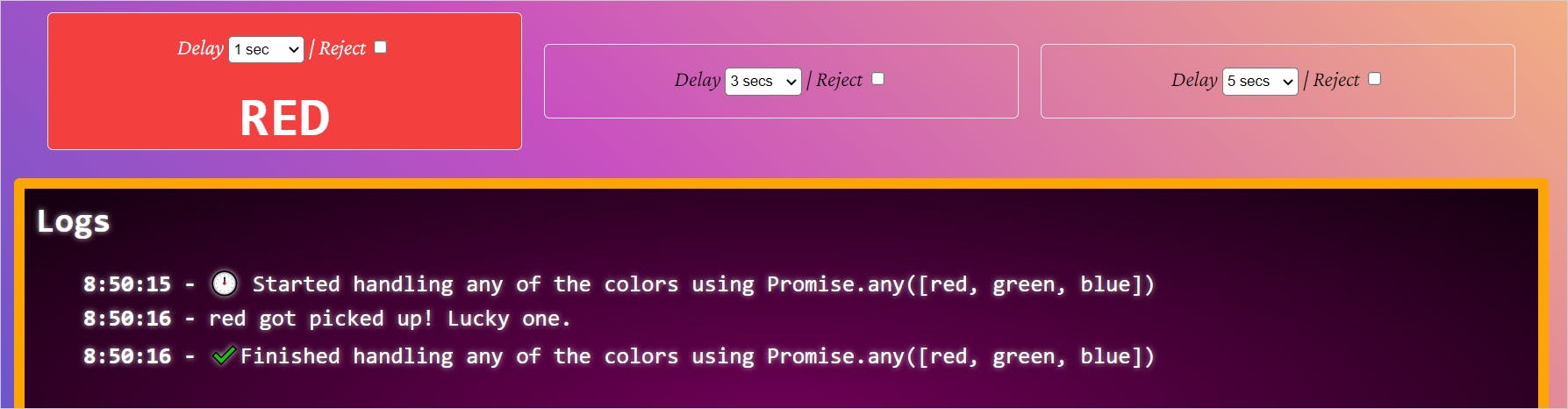
The API method took 1 second to execute the red promise and resolves with it. What happens when you reject the red promise. Let's do it.
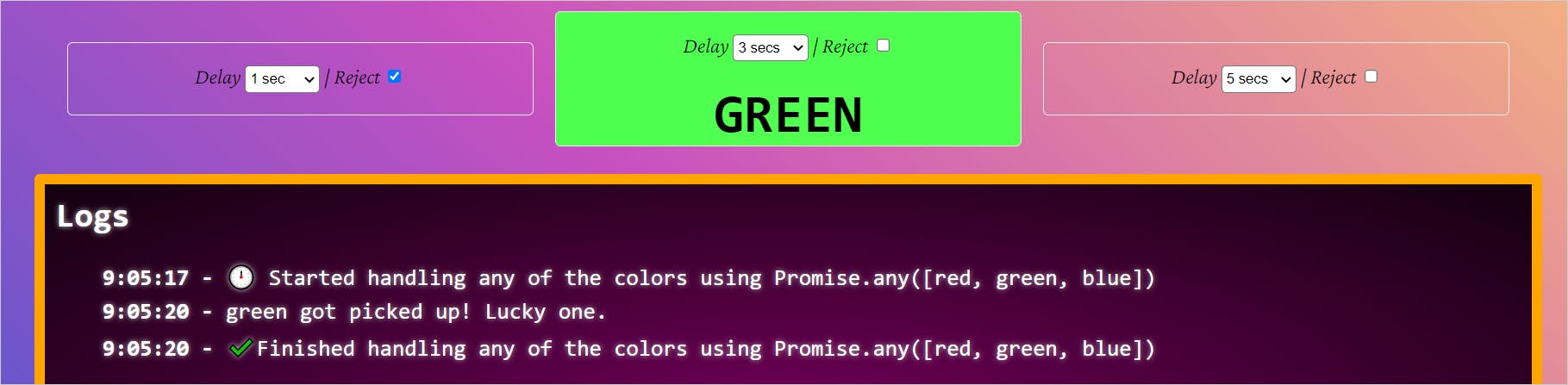
Now, the green promise resolves as it is the next one to pick. If we now reject red and green, the API will resolve the last input promise, blue. Let us now reject all the promises and see what happens.
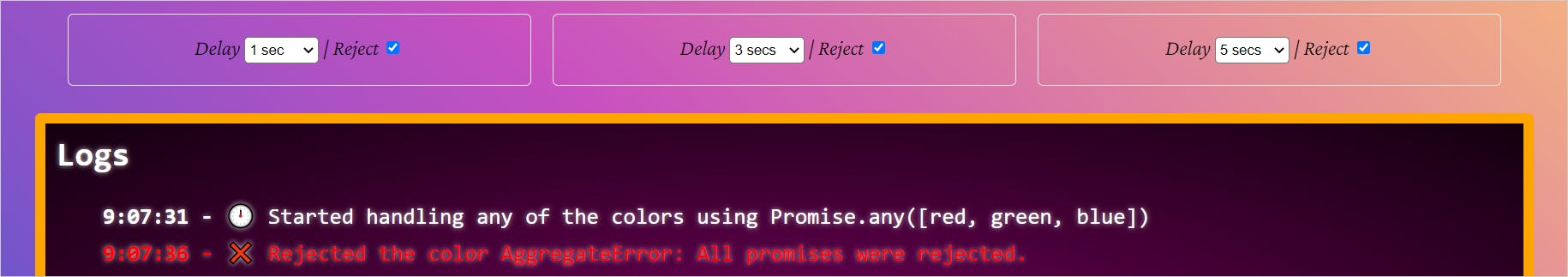
It is AggregateError. Notice the time taken to execute, and it is 5 seconds, the max time taken by an input promise(blue).
Promise.race
As the name suggests, it is the race between all the input promises, and the fastest promise wins! The Promise.race API method accepts a collection of input promises and returns a new promise when the fastest promise resolves.
const testRace = async () => {
const color = await Promise.race([red, green, blue]);
console.log(color);
}
testRace();
In our example, the red promise is the clear winner. It resolves within 1 second.
A point to consider,
- If the fastest promise rejects(or error out), the
Promise.raceAPI method returns a rejected promise. It is a fundamental difference between theracemethod with theanymethod. Theanymethod keeps trying, whereas theraceis all about making the fastest win else all lost.
Let's understand it using PromiViz. Would you please run the Promise.race API method? We see red wins the race in 1 second.
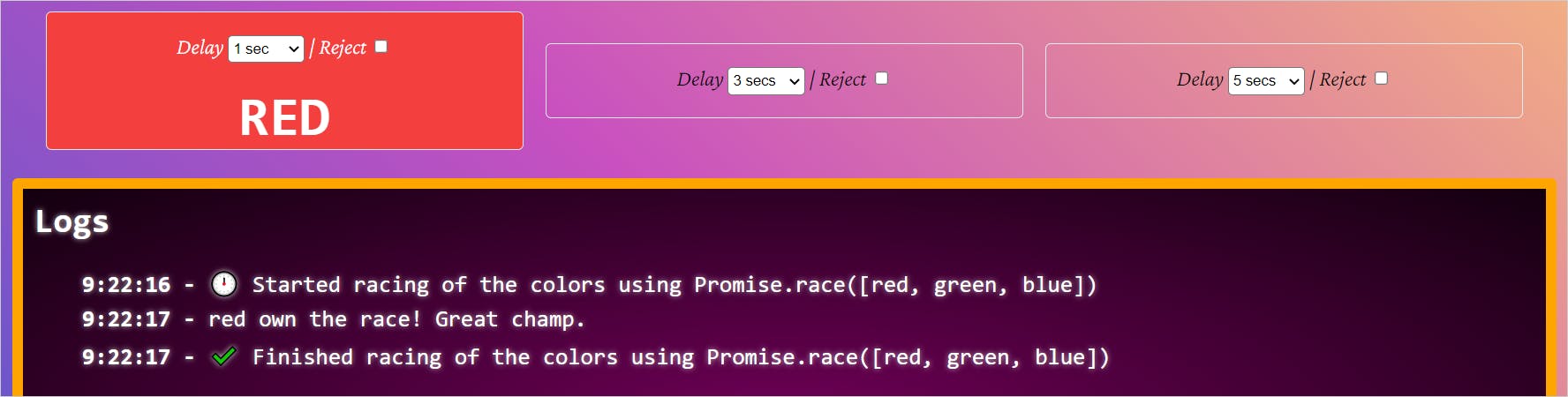
Now adjust the delays. Make it 3 seconds for red, 2 seconds for green. You should see the green winning the race now as it is the fastest.
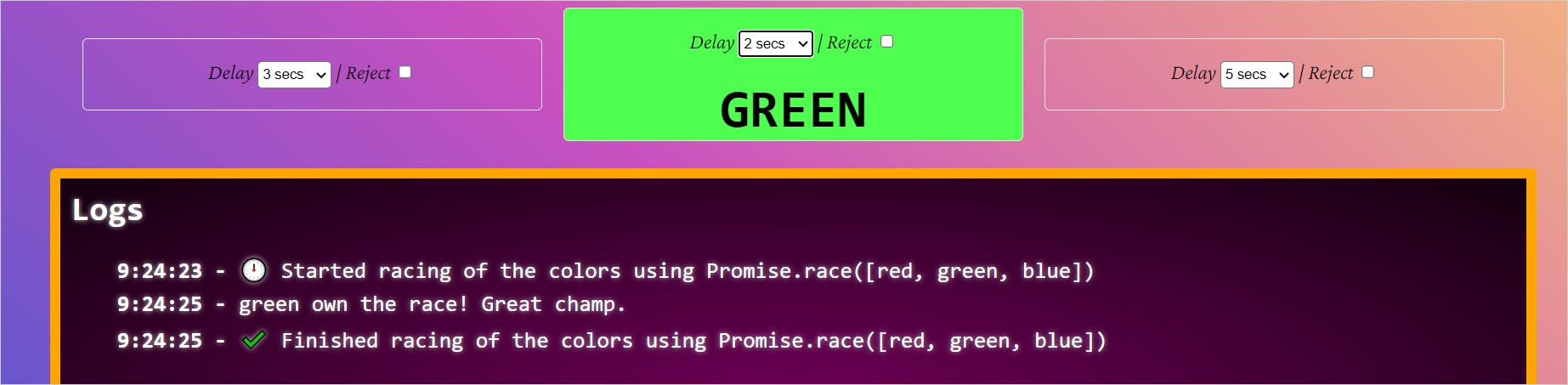
Now reject green. What do you think will happen? You have rejected the fastest promise. So, by rule, the Promise.race will not continue the execution of others. We will get a rejected promise that we need to handle.
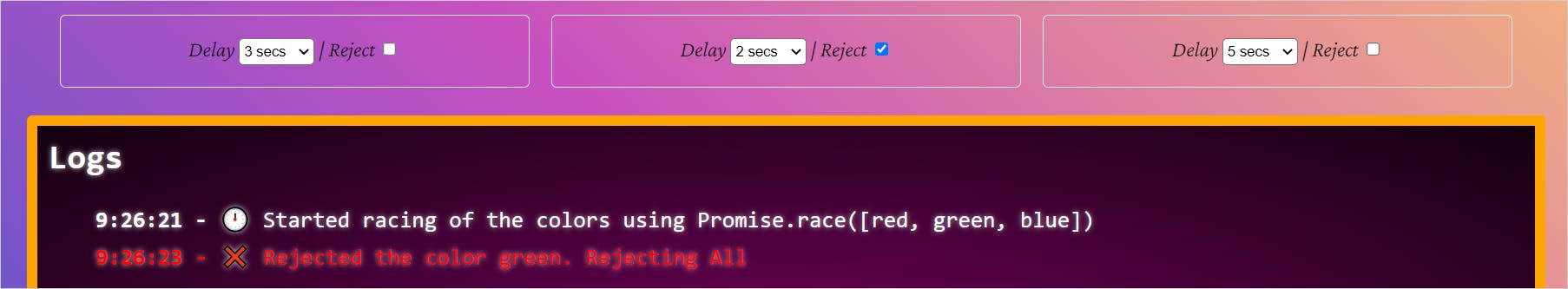
Alright, let's move onto the following important API method.
Promise.allSettled
The Promise.allSettled method is the newest inclusion to the promise API method list. Just like the methods we have seen so far, it takes an array of input promises.
Unlike the Promise.all method, it doesn't reject all if any input promises reject or error out. It continues to execute and returns an array of settled promises, including their state, value, and the reason for an error.
Let's assume the red and green promises resolves successfully and the blue promise rejects due to an error. Let's run Promise.allSettled using these promises,
const testAllSettled = async () => {
const colors = await Promise.allSettled([red, green, blue]);
console.log(colors);
colors.forEach(color => {
console.log(color);
});
}
See the output,

It returns all the settled promises with status, value for a resolved promise, and reason for the rejection for a rejected promise. Here is the execution result of the Promise.allSettled API method using PromiViz. Please note, we reject the blue promise here.
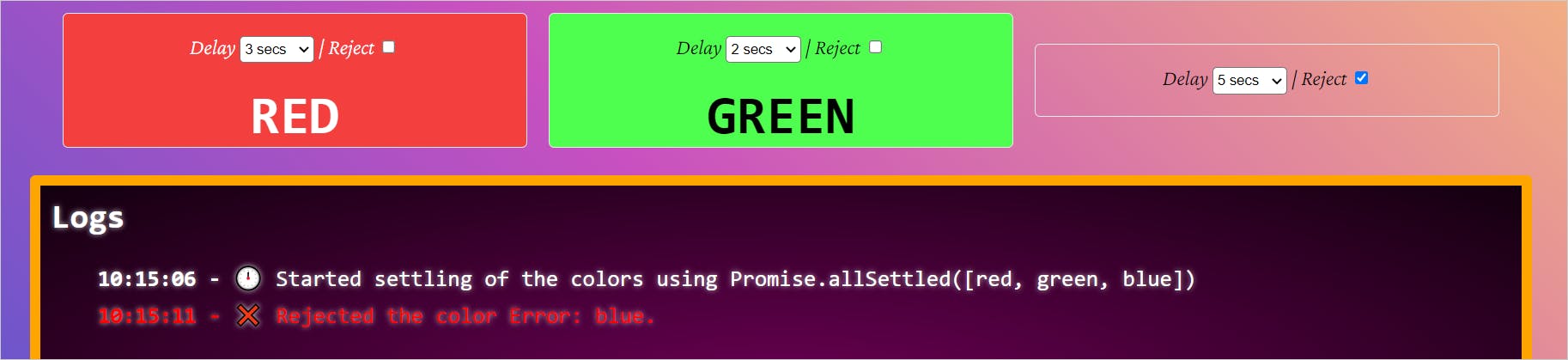
It took the entire 5 seconds to complete execution. It never rejected the other two promises.
Promise.resolve and Promise.reject
The last two methods are Promise.resolve and Promise.reject. The first creates a resolved promise with a value, and the latter creates a rejected promise with an error.
// It resolves with the value green after 3 seconds
const green = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('green');
}, 3000);
});
const resolveOne = async () => {
const result = await Promise.resolve(green);
console.log(result);
}
resolveOne();
In most cases, you would probably prefer using async/await instead of these two methods. However, consider these methods when you create promises manually like this,
new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
resolve(value);
}).then(/* handle it */);
The better and short syntax is,
Promise.resolve(value).then(/* handle it */);
Similarly, for reject,
Promise.reject(value).catch(/* handle it */);
Congratulations!!! You have learned about all the Promise API methods.
Examples and Analogies
Here are some examples and analogies you may find helpful.
| Promise API Methods | Example |
| Promise.all | I am downloading multiple files from different sources. |
| Promise.allSettled | I am downloading multiple files from different sources, and I am okay with whatever was downloaded successfully. |
| Promise.any | I am downloading my profile image of different resolutions from several sources. I am OK with any that I get first. |
| Promise.race | I am downloading my profile images of different resolutions from several sources. I want to get the fastest one to proceed. |
So, What's Next?
We have come a long way in understanding the core concepts of asynchronous programming in JavaScript. To recap, we learned about,
- The JavaScript Promises, how to resolve and reject them
- How to tackle promises with the Promise Chain, how to handle errors
- Async/Await keywords and their togetherness with plain-old promises
- Promise API methods in this article.
Thank you for letting me know, you are enjoying the series so far. Next, we will learn about the common mistakes we make with promises and get better at answering the interview questions. Until then, you can look into the source code used in the article from this repository and try it out using PomiViz.
I hope you enjoyed this article or found it helpful. Let's connect. Please find me on Twitter(@tapasadhikary), sharing thoughts, tips, and code practices. Would you please give a follow? You can hit the Subscribe button at the top of the page to get an email notification on my latest posts.